Sustainable Water Use At Port Terminals
Water is a valuable resource that can no longer be taken for granted and needs to be managed judiciously through measures to conserve, recover and reuse, especially in industries that consume large quantities of water. Ports are often significant consumers of water due to the nature of their operations and the various activities that require water. Hence, implementing sustainable measures at port terminals is crucial for minimising water consumption, reducing the extraction of freshwater resources, and minimising the discharge of wastewater into surrounding waters. Water conservation can be achieved at ports through a combination of water-efficient infrastructure, behavioral change through education and awareness, rainwater harvesting, water recycling and reuse.
The ‘Harit Sagar’ Green Port Guidelines laid down by the Government of India focuses on adopting the following parameters for pushing water suitability measures:
| Harit Sagar Guidelines | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase the capacity of water treatment plants and usage of treated water. | Achieve more than 20% reduction in freshwater consumption for every ton of cargo and 100% recycle & reuse wastewater by year 2030. | ||||||
| Explore the possibility of installation of desalination plants as an alternate to ground / surface water. | Make adequate arrangements for rainwater harvesting for effective collection of rain water wherever possible. | ||||||
Driven by the aim to achieve sustainable growth in the industry, J M Baxi Ports & Logistics is focusing on a three-point approach framework which can be adopted to enhance sustainable water management practices. The guiding principle is to reduce water consumption, minimize environmental impact, and contribute to long-term water resource sustainability. This framework involves focusing on three key areas
Water efficiency
Focuses on optimising water use and reducing wastage through
- Implementation of water-efficient
technologies and equipment
Integrating green infrastructure, utilise low-flow fixtures, water- saving appliances, and water- efficient irrigation systems. - Conduct regular water audits
Assess water consumption patterns, identify areas of high usage, and implement measures to minimise wastage. - Promote behavioural change
Educate project stakeholders about water conservation practices and encourage responsible water use.
Water conservation
This aspect involves preserving water resources and minimising environmental impact through
- Rainwater harvesting
Collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as landscaping, cleaning, or construction activities. - Water recycling and reuse
Treat and reuse wastewater generated within the project for purposes like irrigation, equipment cooling, or toilet flushing. - Implement stormwater
management strategies
Use techniques like permeable pavements, green infrastructure, and retention ponds to manage stormwater runoff and reduce pollution.
Water stewardship
Focuses on actively managing and protecting water resources through
- Environmental monitoring
Regularly monitor water quality, assess impact on nearby water bodies, and ensure compliance with applicable regulations. - Engage with stakeholders
Collaborate with local communities, authorities, and experts to ensure a holistic approach to water management and address concerns. - Continual improvement
Set targets, measure performance, and regularly review water management strategies to identify opportunities for improvement and innovation.
Water saving initiatives undertaken at J M Baxi Terminals
At J M Baxi terminals, water is mostly withdrawn from third-party water providers and in some places from groundwater. Water is mainly used for cleaning and maintenance, office buildings and canteens. The company is committed to managing and working towards reducing its water footprint. All business units are advised to adopt necessary measures as per regulations, to manage wastewater and ensure wastewater release complies with necessary legal requirements before discharge.
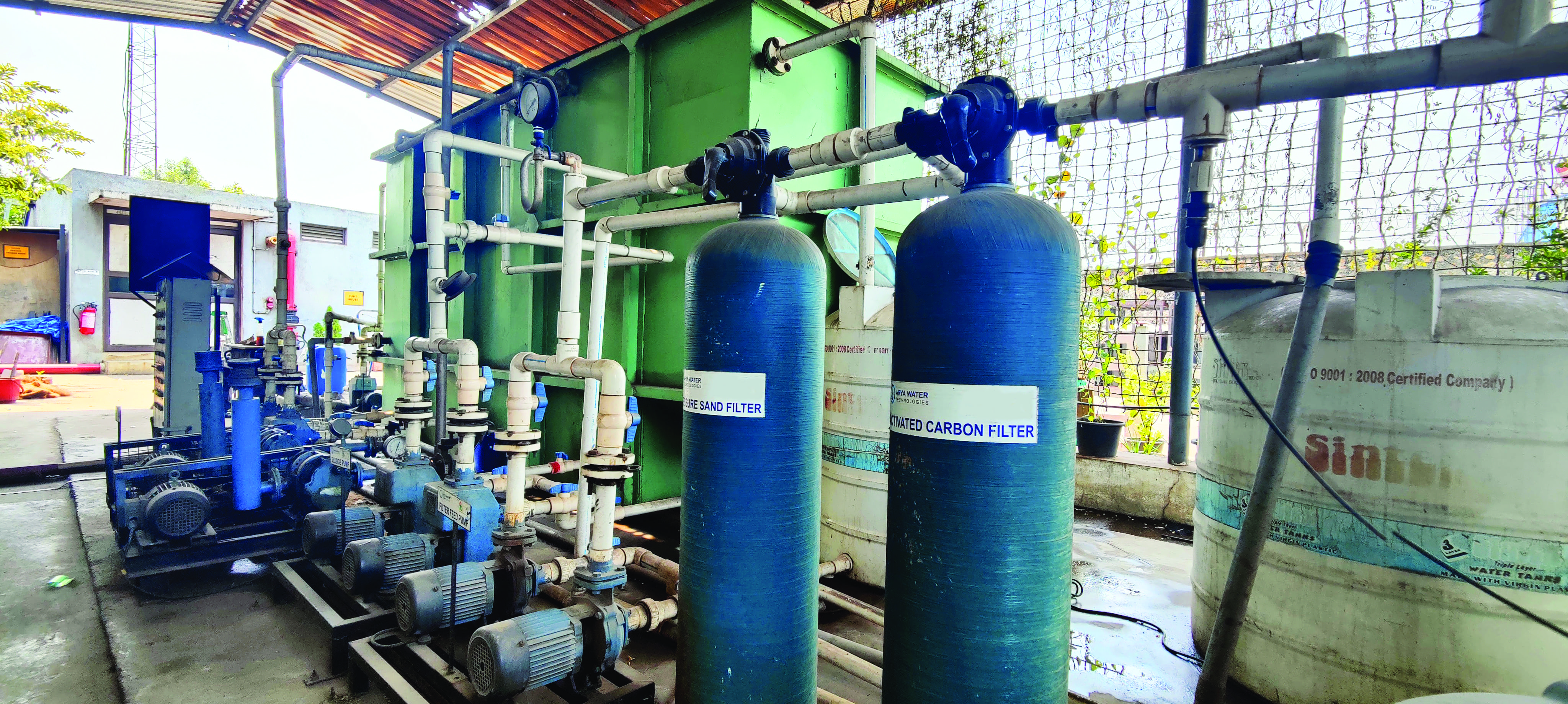

STP plant at Visakha Container Freight Station
Water reduction initiatives include
- Water usage monitoring processes
Adopting efficient water management measures such as monitoring monthly water consumption with flow meters and installing fixed water meters in different areas for equipment/ container cleaning and drinking. At Haldia Container Terminal water meters are installed in workshop areas, the project and engineering building and at the terminal. - Employee awareness sessions for behavioral changes on water conservation
Creating awareness among employees, workers and operators about water usage, maintaining records and efficient water consumption practices. - Water filtration plant
Installation of Reverse Osmosis (RO) plant for purifying and desalinating water, making it suitable for various applications, including drinking water, irrigation etc. At Delhi Inland Container Terminal - Sonipat, an RO plant is installed with a capacity of 500 litres per hour for the supply of drinking water for the entire terminal and the rejected RO water is used for flushing purposes. - Enhancing uses of recycled water from STPs
Recycled water can be used for gardening, flushing, washing of equipment and cleaning of solar panels. At Visakha Container Freight Station, a single Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) unit of 16.5 kilolitre (kl) capacity is installed. 10 kl of STP water is generated daily, and used for gardening through drip irrigation and ~ 5kl of water is stored in a collection tank of an STP unit. - Rainwater harvesting
Port terminals can collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses. At Delhi Inland Container Terminal around 21 Rainwater Discharge Pits (RWDP) cover the entire facility premises. The Storm Water (SW) Drain is connected through a de-silt chamber to the RWDP. The water is drained through a perforated PVC pipe driven 8 to 10 feet above the ground water table. Through perforated sheets, the water is dispersed, and charges the underground water table to harvest more than 900 kl per annum. - Usage of brown water
Recycled brown water is also used for firefighting purposes.
The above measures are helping achieve a 13.5 percent Y-o-Y reduction in total water consumption across all our terminals.
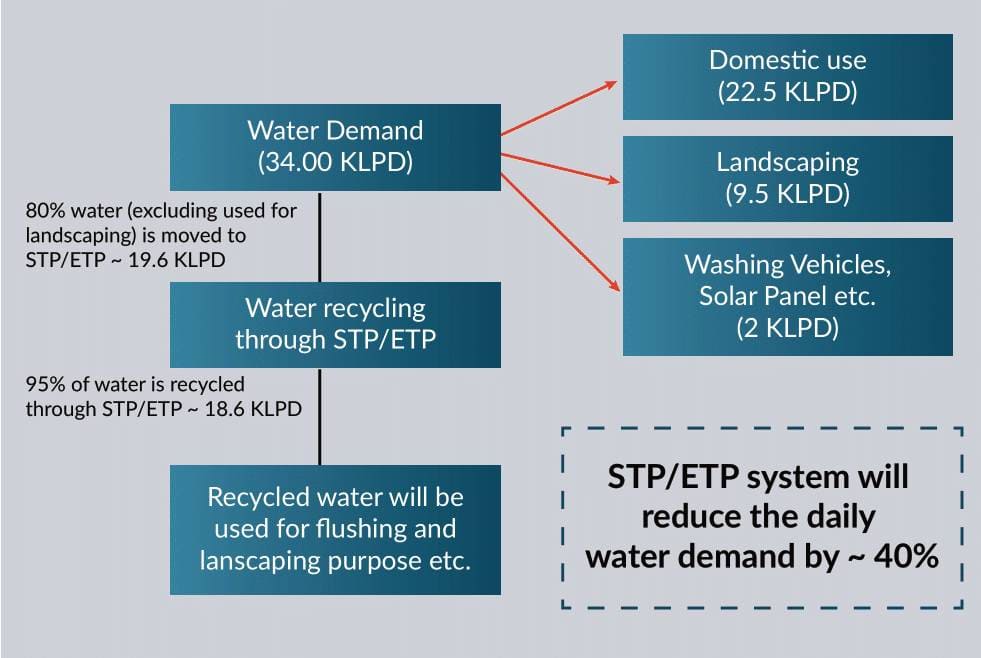
Initiatives for water sustainability at the upcoming Tuticorin Container Terminal The projected demand for water consumption is determined, and water recycling is envisaged through the adoption of STP/ Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP).
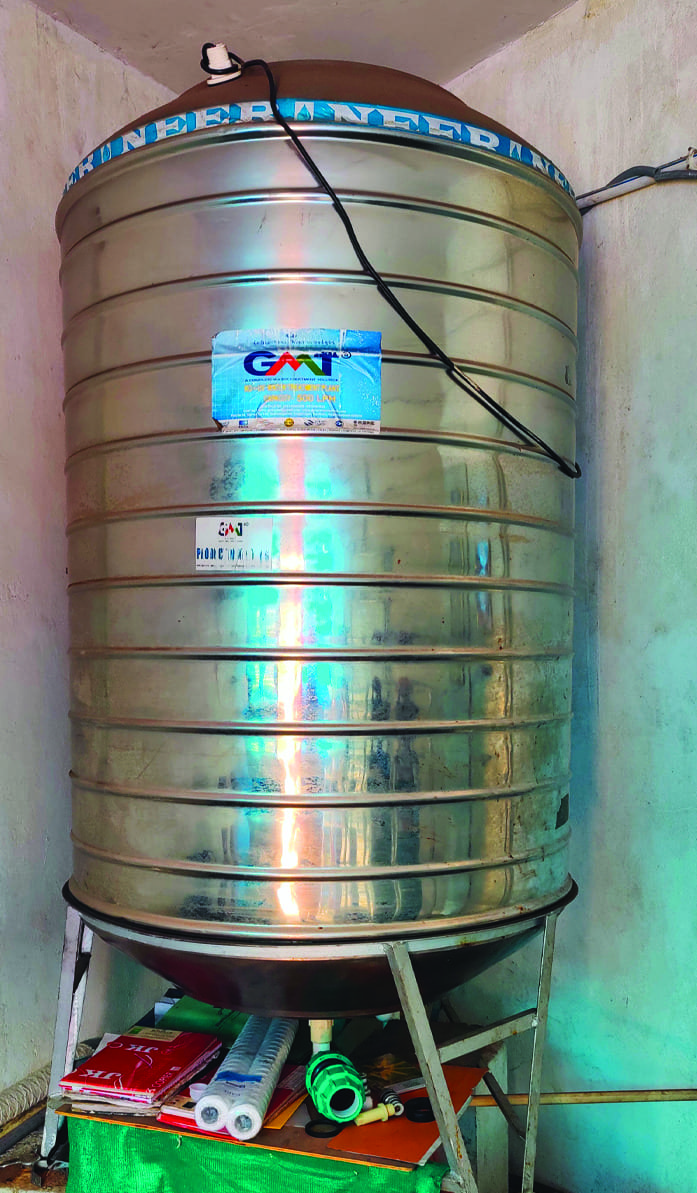

RO plant at Visakha Container Freight Station
| Project details - Tuticorin | |
|---|---|
| Item | Description |
| Water requirement | Water demand of ~ 34 kilolitres a day (KLD) is envisaged during the operation stage. This demand will be generated through domestic use, machinery and equipment washing and watering in landscaping area. |
| Sewage treatment plant | A zero liquid discharge STP system would be planned near toilet blocks and the building area. An STP of 10 KLD would be planned near admin building and another two compact STPs of 5 KLD capacity near the workshop and labour shed area. The provision for storage of treated water is also kept near each location of the proposed STP. The reuse of water through STP will reduce the daily water demand by ~40 percent |
| Effluent treatment plant | The compact size of the effluent treatment plant of ~2 KLD capacity is planned near the workshop at the rubber tyre gantry (RTG) washing area. |
| Rainwater harvesting | Underground tanks are proposed at 3 locations to store rainwater |
| Oil water separator | Planned near ETP plant next to the RTG washing area and workshop. |
| Zero liquid discharge | All STPs of zero liquid discharge are planned. |

Rain water harvesting pit at Delhi Inland Container Terminal.