5G is all the buzz and is expected to be launched later this year. Here is a ready reckoner of all you need to know about this next gen technology
- Where does 5G get it’s name from?
5G is so named because it's the fifth generation of wireless networking technology. It can provide higher speed, lower latency and greater capacity than the 4G LTE network.
- Why was 5G made?
5G is designed to not only deliver faster, better mobile broadband services compared to 4G LTE, but can also expand into new service areas such as mission-critical communications and connecting the massive Internet of Things (IoT).
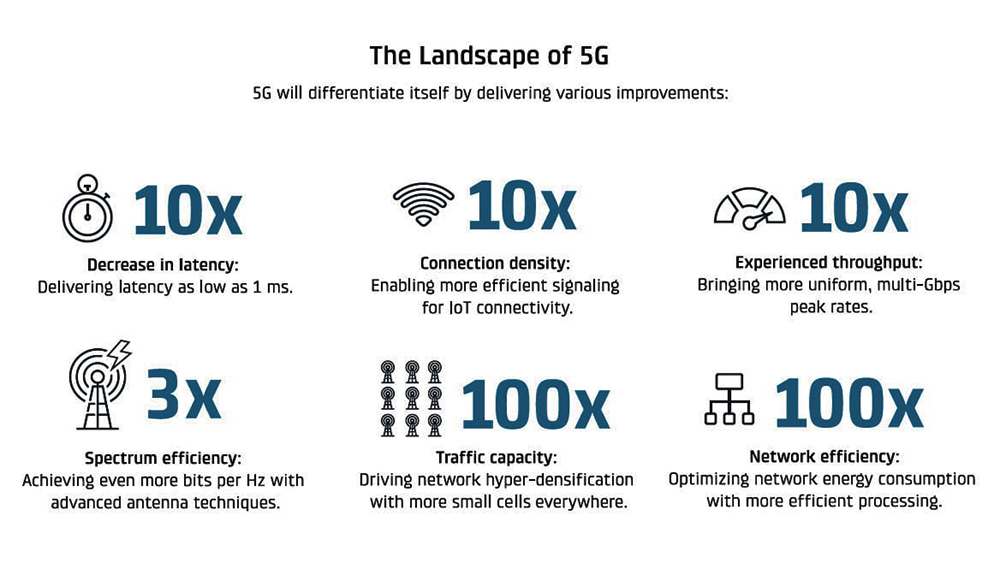
- What new technology does 5G use?
5G is based on Orthogonal frequencydivision multiplexing (OFDM), a method of modulating a digital signal across several different channels to reduce interference. 5G uses 5G New Radio (NR)air interface alongside OFDM principles. 5G also uses wider bandwidth technologies such as sub-6 GHz and Millimeter Wave (MM Wave).
| Developed by |
| 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is an umbrella term for a number of standards organizations which develop protocols for mobile telecommunications |
| Introduced |
| July 2016 |
| Industry |
| Telecommunications |
- What spectrum does 5G use?
One of the more confusing aspects of 5G is that it's not broadcast on a single frequency. Instead, there are several frequencies used by 5G networks for different applications.
To get that speed, 5G networks rely on much higher operating frequencies than existing cellular networks, reaching into what is called the MM Wave band. Low-band 5G operates between 600-850 MHz. This is similar to what 4G networks currently use and is only moderately faster than 4G, between 50-250 Mbps offering similar coverage areas for each cell tower.
Mid-band 5G operates in the 2.5- 3.7 GHz range and delivers speeds between 100-900 Mbps. While offering less range per cell tower, this type of 5G is going to be the most common implementation of 5G networks for many years to come.
High-band 5G is the band that is most commonly associated with 5G. Operating at 25-39 GHz, this is known as MM Wave spectrum and delivers gigabit speeds currently tested as high as 1.8 Gbps. The trade-off is that MM Wave transmitters have a very limited range and require the deployment of many small transmitters, so it's only viable in urban areas where transmitters can be near closely spaced homes and buildings.
- How many countries have 5G so far?
According to the Ookla® 5G Map™, there were 5G deployments in 112 countries as of November 30, 2021. That's up from 99 countries on the same date a year ago.
- What is difference between 4G and 5G?
The key difference between 4G and 5G is speed — 4G can currently reach top speeds of up to 100 Mbps, though realworld performance is generally no more than 35 Mbps. 5G has the potential to be 100 times faster than 4G, with a theoretical top speed around 20 Gbps and current, real-world speeds from 50 Mbps to 3 Gbps.
- What are the disadvantages of 5G?
The main disadvantage of 5G is that it has limited global coverage and is available only in specific locations. Only cities can benefit a lot from 5G networks and remote areas may not get this coverage for some years. Moreover, the expenses for setting tower stations are high when compared to other networks.
- How far should you be from a 5G tower?
5G Range. The trade-off for speed at MM Wave frequencies is limited range. Testing of 5G service range in MM Wave has produced results approximately 500 meters from the tower, meaning a huge propagation of Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO)-enabled antenna arrays would be required for pure standalone 5G deployment. MIMO is a wireless technology that uses multiple transmitters and receivers to transfer more data at the same time.
- Which sectors will benefit the most from the realisation of 5G?
- Manufacturing
- Agriculture
- Healthcare
- Transport
- Education
| COMPARING 4G TO 5G | ||
|---|---|---|
| 4G | 5G | |
| Latency | 200 milliseconds | 1 millisecond |
| Data Rate | 100x Improvement | |
| Millimeter Wave Spectra | Supports 4000 devices/sq. km | Supports 1 million devices/sq. km |
| Speed | 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| IoT device Performance | Battery life of low-power devices will increase up to 10 yrs. | |
5G is set to enable large scale 'machine to machine' communications, allowing for a reduction in human error and an increase in automated processes.
- How will 5G affect cybersecurity?
5G's dynamic software-based systems have far more traffic routing points than the current hardware-based, centralized hub-and-spoke designs that 4G has. Multiple unregulated entry points to the network can allow hackers access to location tracking and even cellular reception for logged-in users.
- Do airplanes use 5G?
Carriers are using C-band spectrum to provide 5G service at full speed, 10 times the speed of 4G networks. The C-band spectrum is close to the frequencies used by key electronics that aircraft rely on, to land safely.
- How is the 5G scenario in India
Airtel said it conducted India's first rural 5G trial with Swedish telecom equipment maker Ericsson, on the outskirts of Delhi. Bharti Airtel has said that the first 5G network will be launched within two-quarters of the spectrum auction and can cover a large part of the country after one year. Department Of Telecommunications (DOT) confirmed in a press release that 5G services will be available in up to 13 cities across the country in 2022, including Delhi, Gurugram, Bengaluru, Kolkata, Chandigarh, Jamnagar, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Hyderabad, Lucknow, Pune and Gandhi Nagar. The three largest telecommunications providers Jio, Airtel, and Vodafone Idea (Vi) have already set up 5G test sites in these cities.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi could launch a 5G network on India’s 75th Independence Day, according to a news report.
